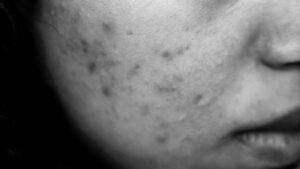
Hyperpigmentation is when skin becomes darker than normal, even in light skin tones. It can be caused by a number of things, such as sun damage, hormonal changes, or lifestyle factors.
This post is all about Hyperpigmentation in the Skin.
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that makes some parts of the skin darker than others. It occurs when the skin produces an excessive amount of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Spots or patches might appear brown, black, grey, red, or pink due to the excess melanin produced in the skin. When it comes to hyperpigmentation, all skin types are affected, however, it is particularly noticeable in people with darker skin tones.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
Among the many types of hyperpigmentation, the most common are dark spots (also known as sunspots), melasma, freckles, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Sunspots: Also called solar lentigos, age spots, or dark spots, these hyperpigmented lesions are brown to black skin defects mostly common in middle-aged adults. They appear on sun-exposed regions of the body (particularly the hands, arms, and face), and are most likely the result of persistent UV exposure and the resulting chronic inflammation. It often affects older people or those who have been exposed to the sun for an extended period.
- Melasma/chloasma: Melasma is a skin condition that manifests as darker-than-normal patches and spots, typically on the face. Women who are pregnant or taking birth control pills are more likely to develop melasma on their skin.
- Freckles: A freckle is a tiny, flat, pale to deep brown patch of skin with a wavy border. People with freckles produce a lot of melanin, but it is not equally distributed across their skin.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Post-inflammatory pigmentation is a transitory discoloration of the skin that occurs due to several different inflammatory conditions (e.g., dermatitis, infection). Pigmentation of the skin is often grey-brown and persistent for many years.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Depending on the different types of hyperpigmentation, there are a wide range of causes.
- Imbalanced Melanin production: The skin tone of an individual is determined by a pigment called melanin that is produced by skin cells. In response to injury, these skin cells create an abundance of melanin. When melanin accumulates in a place, it darkens the region.
- Sunlight exposure: Most hyperpigmentation is caused by excessive sun exposure. The sun stimulates the formation of melanin, and prolonged exposure might result in hyperpigmentation.
- Inflammation of the skin: Any damage to the skin’s dermis or epidermis results in hyperpigmentation. When the skin is inflamed, melanocytes are stimulated to produce more melanin which in turn leads to darker skin tone.
Susceptible Skin types
People with darker skin have a higher risk of developing dark spots. When hormones or injuries cause an increase in the production of melanin in the skin, you are more likely to develop hyperpigmentation as a result. Dark-skinned, Hispanic, and Asian people are more likely to experience melasma or hyperpigmentation.
In women, changes in skin tone can also occur during pregnancy and while using oral contraceptives due to hormonal changes in the body.
Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common yet difficult complication of cutaneous inflammation, especially in people with darker skin. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and melasma affect patients’ quality of life. Treatment is based on the source and extent of dark pigmentation.
- Topical Creams: Hydroquinone is present in most prescription skin-lightening products. It’s possible to use bleaches to lighten and remove dark patches of skin over time by decreasing the formation of melanin. Corticosteroids, such as Tretinoin, may be administered in more severe cases
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels are used to cure discolored skin by removing the top layers of the skin using a chemical solution. This technique resurfaces the skin and improves skin tone.
- Microdermabrasion: This is an epidermal resurfacing process used to treat uneven skin tone and texture, photoaging, sun damage, melasma and scars, such as acne scars.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): IPL is a form of treatment that uses a laser to precisely target and remove pigmented or damaged skin cells. IPL can be used to treat a variety of skin problems.
- Home remedies: Hyperpigmentation can be treated using home remedies that have skin-lightening ingredients. Treatments include using natural components such as turmeric, aloe vera, green tea extract, tomato, apple cider vinegar, milk, and curd.
This post was all about Hyperpigmentation in the Skin.
References
1- Nieuweboer-Krobotova, L. (2012). Hyperpigmentation: types, diagnostics and targeted treatment options. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 27, 2–4. doi:10.1111/jdv.12048
2- Ortonne, J.-P., & Bissett, D. L. (2008). Latest Insights into Skin Hyperpigmentation. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 13(1), 10–14. doi:10.1038/jidsymp.2008.7
3- Woolery-Lloyd H, Kammer JN. Treatment of hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011 Sep;30(3):171-5. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2011.06.004. PMID: 21925372.
4- Leyden, J. J., Shergill, B., Micali, G., Downie, J., & Wallo, W. (2011). Natural options for the management of hyperpigmentation. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 25(10), 1140–1145. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011. 04130.x